December 27, 2024
Multi-Cloud Strategies: A Guide to Staying Strong, Saving Money, and Being Flexible with Platforms

By Priyank Dhami
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
In today’s era, using more than one cloud service is no longer a way to stand out; it’s a strategic need. Flexera’s State of the Cloud Report says that 89% of businesses currently work in more than one cloud. The requirements for resilience, vendor flexibility, regional performance, and financial management are making this change happen.
But it can be hard to deal with all of this complexity, including tools, vendors, governance approaches, and cost visibility. The secret is to use platform engineering, FinOps, and governance-first frameworks to grow the right way while keeping costs and risks low.
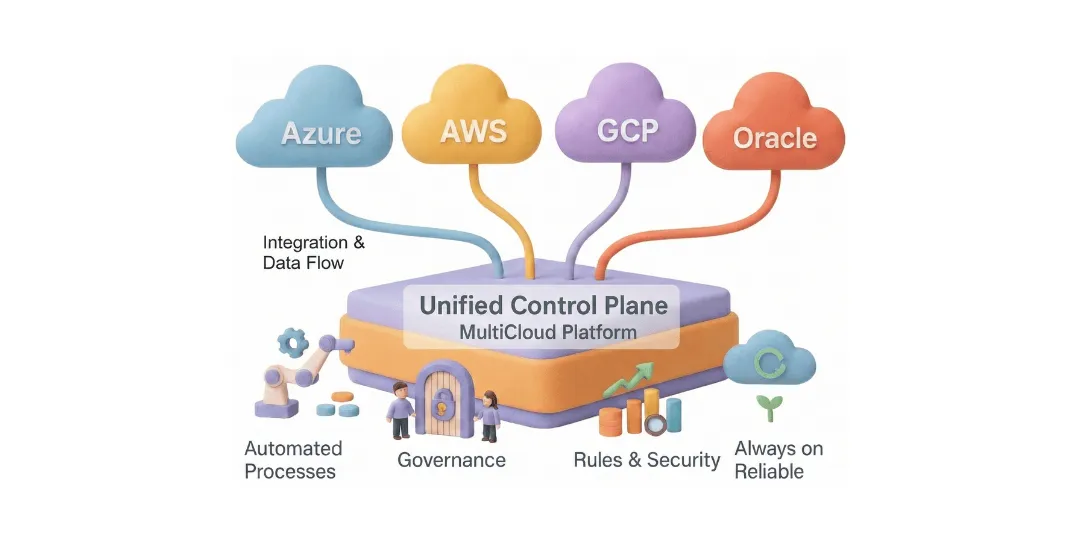
Learning about Multi-Cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud integration means using cloud services from diverse companies to meet a company’s IT needs. More than 84% of businesses are already using multi-cloud strategies to make their businesses more flexible, resilient, and innovative. This technique is growing more common.
Important Parts of Connecting to Multiple Clouds
Multi-cloud strategies help businesses in many ways, including as avoiding vendor lock-in, improving resilience, saving money, and being able to recover from disasters.
What Platform Engineering Does
Infrastructure Abstraction
Platform engineering is very important for hiding the underlying infrastructure from developers. This means making APIs, templates, and automation scripts that let developers work with the infrastructure without having to know how it works.
Platform engineers streamline operations by building solutions that automate tasks like provisioning virtual machines, deploying containerized apps, or setting load balancers. This is possible thanks to APIs and automation scripts that hide the complexity of the infrastructure. Platform engineers make sure that teams, apps, and infrastructure are all the same by creating standard environments, tools, and workflows. This makes it easier to handle different cloud environments efficiently.
Automating daily tasks
Platform engineers are in charge of automating a lot of the operational duties that operations teams used to do by hand.
Provisioning and Scaling: By automating operations like setting up infrastructure and expanding apps, you don’t have to do as much human work, which lowers operating costs. This mechanism makes sure that resources are assigned dynamically based on demand, which eliminates over-provisioning and underutilization.
Monitoring and Setting Up: Automated monitoring and setup of environments helps in keeping the systems running well and makes sure they are always available and can handle faults.
Working with several cloud environments: Platform engineers need to make platforms that work well with a lot of different cloud settings.
Vendor-Agnostic Tooling: Platforms are made to function with more than one cloud provider, so businesses may use the same apps in different settings without having to stick with one vendor. VMware vRealize, HashiCorp Terraform, and Microsoft Azure Arc are some of the tools that help manage and connect many clouds.
Consistency Across Clouds: Platform engineers make sure that apps run the same way in all cloud settings by giving developers the same tools and processes to use. This consistency is really important for keeping things running smoothly and making things less complicated.
Why Multi-Cloud Will Be Important
Companies choose multi-cloud to:
- Keep from being locked into a single vendor
- Make applications more reliable in different places
- Place workloads in the cloud to get the best prices.
- Follow all rules and regulations
But there are some trade-offs:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| No vendor lock-in | Higher complexity |
| Improved resilience | Tool sprawl and siloed teams |
| Geo-redundancy | Increased governance demands |
| Pricing flexibility | Visibility and security fragmentation |
To make a multi-cloud strategy work, you need to find the right tools, think about platforms, and give developers the tools they need.
Making the most of your money in multi-cloud settings
To grow without spending too much, businesses need to make cost-awareness a part of their architecture and operations.
Important things to do:
- Make sure you have the right amount of resources: Keep changing the sizes of instances to fit their use.
- Use Spot or Preemptible instances to save up to 90% on workloads that aren’t important.
- Billing arbitrage is running workloads that cost a lot in areas or with providers that cost less.
- Include cost in CI/CD and engineering KPIs to make FinOps culture a part of your business.
Tools that are suggested:
CloudZero, nOps, Kubecost, AWS Cost Explorer, and GCP Cost Management are all examples of cloud cost management tools.
Architectural Complexity and Management:
Organizations need to focus on centralized management and automation to make it easier to run multi-cloud infrastructures. To keep sensitive data safe, you need strong security measures, including consistent policies, constant monitoring, and DevSecOps processes. For efficient resource management, it is important that different cloud platforms can work together without any problems. Cloud orchestration technologies make this possible. To make sure that resources are used as efficiently as possible and costs are kept to a minimum, performance monitoring and cost optimization are very important. Finally, to keep the business going and strong, you need strong backup and disaster recovery plans, such as multi-cloud failover and recovery plans.
Today’s Workloads
- Containerization and Kubernetes: Use containers to make deployment and management easier.
- Use serverless functions for workloads that can grow and don’t cost a lot.
- Edge Computing and AI: Look at edge computing for applications that need low latency and AI-driven optimization.
- Data Management and Governance: Set up rules for classifying, protecting, and governing data.
Tools and Methods for Managing Multi-Cloud Platforms
Platform and DevOps teams can make things easier by using orchestration, monitoring, and policy automation.
Best Tool Types:
- Infrastructure-as-Terraform (HashiCorp) Code:
- GCP Anthos, Azure Arc, and AWS Proton are all orchestration tools.
- Cost and FinOps Tools: CloudZero, Kubecost, and nOps
- Backstage and Kratix are two internal dev platforms.
These technologies help with:
- Setting up resources in one place across clouds
- Enforcement of policies
- A unified experience for developers
- Tracking costs in real time
Management of Governance and Risk
Drift, misconfigurations, and identity fragmentation can all happen in multi-cloud settings. Governance needs to be proactive and built in.
Best ways to do things:
- Use Zero Trust security in all clouds
- For IAM, use CIEM (Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management) tools.
- Use the same rules for tagging every time.
- Allow monitoring for drift and abnormalities in real time
Sonrai Security, Saviynt, Axiomatics, and CloudGuard Cloud Management Tools are some of the tools.
6-Step Framework for the Implementation Roadmap
- Check to see what your company and compliance needs are.
- Define governance: IAM, tagging, and cost attribution
- Choose Tools: Terraform, CloudZero, Azure Arc, etc.
- Include FinOps: alerts, budgeting, and finding anomalies
- Train teams in platform engineering, security, and finance.
- Every three months, look at cost, performance, and risk.
Rates of Adoption
More than 84% of businesses have said they are using a multi-cloud strategy because they want to save costs, make their businesses more flexible, and get the finest services from numerous providers. In the upcoming years, more than 85% of businesses will follow a cloud-first strategy, and more than 50% will use multi-cloud strategies to promote corporate growth and digital transformation.
Examples of Use in the Real World
- Netflix uses AWS and GCP to make sure that their services are always available.
- Airbus divides workloads among providers to get the best latency for each location.
- Finder (Australia) saved between 12% and 50% on costs by leveraging multi-cloud cost arbitrage.
Conclusion: From disorder to order
In today’s era, it’s not about “if” you can use several clouds, but how well you can do it. Companies that adopt platform engineering, FinOps integration, and security-first governance will be able to grow without worry.
Checklist for Multi-Cloud Action
- Look at the apps and clouds you already have
- Set up a governance architecture that works across all clouds
- Set up FinOps dashboards and budgets
- Allow policies for Spot/Preemptible and right-sizing
- Use platform tools to make deployments the same every time.
- Teach teams how to be responsible for costs and cloud security
Do you need help building your multi-cloud plan? Talk to Improwised about cloud infrastructure that is platform-driven, cost-aware, and secure.
Frequently Asked Question
Get quick answers to common queries. Explore our FAQs for helpful insights and solutions.


By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.


By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.


By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Optimize Your Cloud. Cut Costs. Accelerate Performance.
Struggling with slow deployments and rising cloud costs?
Our tailored platform engineering solutions enhance efficiency, boost speed, and reduce expenses.
