March 31, 2024
A Complete Guide to Traefik with Automatic TLS: Simplifying Kubernetes Ingress Management

By Rakshit Menpara
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
When you have to deal with a lot of services, SSL certificates, and load balancing demands, it can be hard to keep track of traffic flow in Kubernetes clusters. You’re not the only one who has had trouble with sophisticated ingress settings or spent a lot of time trying to find out how to renew certificates.
This full post will teach you how to utilize Let’s Encrypt to manage your TLS certificates automatically and set up Traefik as your Kubernetes ingress controller. When you’re done reading this article, your system will be able to automatically handle SSL certificates and provide traffic to your apps rapidly.
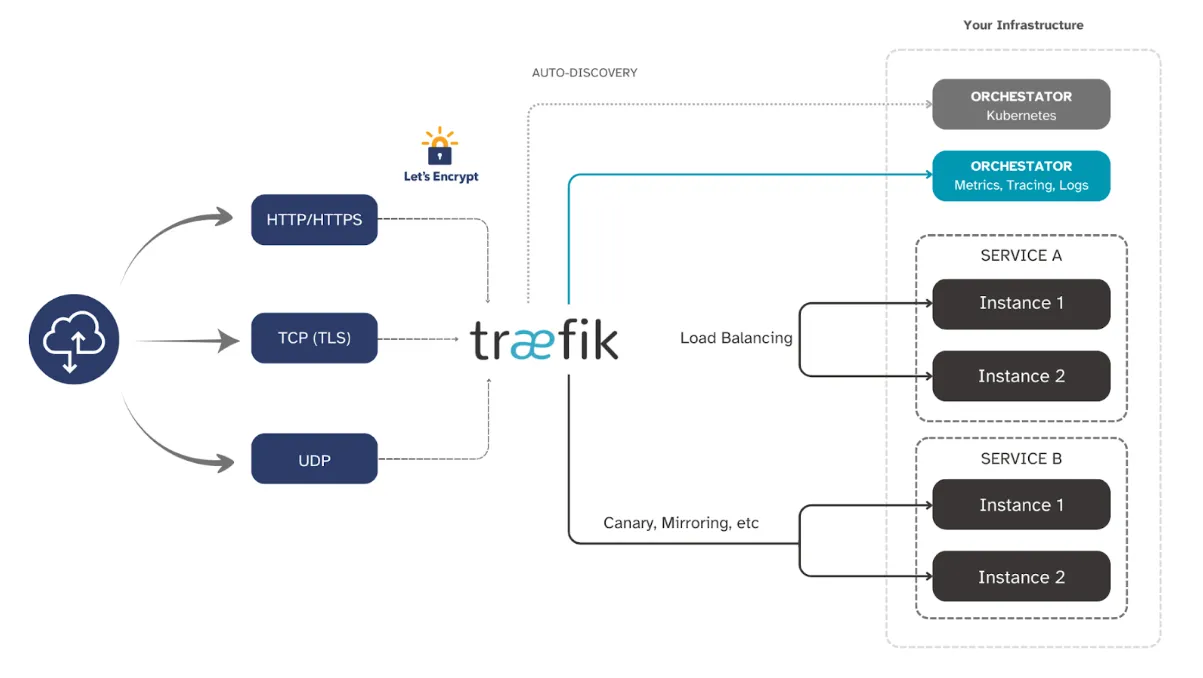
Why is Traefik the best option for Kubernetes Ingress?
With classic ingress controllers, you usually have to set up and manage certificates by hand.
Automatic Service Discovery is a feature of Traefik that changes this. You don’t have to do anything for Traefik to discover your Kubernetes services and set up routing rules.
Built-in Let’s Encrypt, Putting things together: No longer having to manage difficult certificate operations or renew certificates by hand.
Dynamic Configuration: You don’t have to restart the ingress controller to alter your services straight away.
Architecture of Today: A design that works in the cloud with microservices and container orchestration technologies.
How to set up Kubernetes Ingress
Before you start using Traefik, make sure you have:
- A Kubernetes cluster that is already up and running (1.19 or later)
- You have Helm 3.x on your PC.
- Set up kubectl to connect to your cluster
- A domain name you own that points to your cluster’s public IP address
- Cluster admins can install CRD with these permissions
If you utilize a managed Kubernetes service like EKS, GKE, or AKS, make sure that your cloud provider can handle your LoadBalancer service type.
Step 1: Installing Traefik Using Helm
The fastest way to get Traefik running in your Kubernetes cluster is through Helm. Let’s start by adding the official Traefik repository:
# Add Traefik Helm repository
helm repo add traefik https://traefik.github.io/charts
# Update your local Helm chart repository cache
helm repo updateNext, create a custom values file to configure Traefik with Let’s Encrypt support:
# traefik-values.yaml
logs:
general:
level: INFO
access:
enabled: true
# Enable the Traefik dashboard
ingressRoute:
dashboard:
enabled: true
# Configure the service type
service:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
# AWS specific annotations (adjust for your cloud provider)
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: "nlb"
# Let's Encrypt configuration
certificatesResolvers:
letsencrypt:
acme:
email: "your-email@domain.com" # Replace with your email
storage: "/data/acme.json"
keyType: "RSA4096"
tlsChallenge: {}
# Alternative: HTTP challenge
# httpChallenge:
# entryPoint: web
# Persistent volume for ACME certificates
persistence:
enabled: true
size: 128Mi
path: /data
# Resource limits (adjust based on your needs)
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 50Mi
limits:
cpu: 300m
memory: 150MiNow install Traefik with your custom configuration:
# Create a dedicated namespace
kubectl create namespace traefik-system
# Install Traefik
helm install traefik traefik/traefik \
--namespace traefik-system \
--values traefik-values.yamlStep 2: Configuring DNS for Your Ingress Controller
After installation, you need to configure DNS to point to your Traefik service. First, get the external IP or hostname:
\# Get the LoadBalancer IP/hostname
kubectl get svc traefik \-n traefik-system
\# For AWS ELB, use this command to get the hostname
kubectl get svc traefik \-n traefik-system \-o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress\[0\].hostname}'Create DNS records pointing your domain to this IP/hostname:
- A Record:
your-domain.com→LoadBalancer IP - CNAME Record:
*.your-domain.com→your-domain.com(for wildcard subdomains)
Important: DNS propagation can take up to 24 hours, but typically completes within a few minutes to an hour.
Step 3: Deploying a Sample Application
Let’s deploy a simple application to test our Traefik setup. We’ll use a basic nginx deployment:
# sample-app.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sample-app
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sample-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sample-app
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 16Mi
limits:
cpu: 50m
memory: 32Mi
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sample-app-service
namespace: default
spec:
selector:
app: sample-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
Apply the deployment:
kubectl apply -f sample-app.yamlStep 4: Creating Ingress Routes with Automatic TLS
Now comes the exciting part - creating an IngressRoute that automatically provisions TLS certificates:
\# ingress-route.yaml
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: sample-app-ingress
namespace: default
spec:
entryPoints:
\- websecure \# HTTPS entry point
routes:
\- match: Host(\`app.your-domain.com\`) \# Replace with your domain
kind: Rule
services:
\- name: sample-app-service
port: 80
tls:
certResolver: letsencrypt
\---
\# HTTP to HTTPS redirect
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: sample-app-redirect
namespace: default
spec:
entryPoints:
\- web \# HTTP entry point
routes:
\- match: Host(\`app.your-domain.com\`)
kind: Rule
services:
\- name: sample-app-service
port: 80
middlewares:
\- name: https-redirect
\---
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: Middleware
metadata:
name: https-redirect
namespace: default
spec:
redirectScheme:
scheme: https
permanent: true
Apply the ingress configuration:
kubectl apply \-f ingress-route.yamlStep 5: Advanced Middleware Configuration
Traefik’s middleware system allows you to add powerful features to your ingress routes. Here’s a security-focused middleware configuration:
# security-middleware.yaml
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: Middleware
metadata:
name: security-headers
namespace: default
spec:
headers:
customRequestHeaders:
X-Forwarded-Proto: https
customResponseHeaders:
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-Frame-Options: DENY
X-XSS-Protection: "1; mode=block"
Strict-Transport-Security: "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains"
Referrer-Policy: "strict-origin-when-cross-origin"
---
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: Middleware
metadata:
name: rate-limit
namespace: default
spec:
rateLimit:
burst: 100
average: 50Update your IngressRoute to use these middlewares:
\# Enhanced ingress with security middleware
apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1
kind: IngressRoute
metadata:
name: sample-app-secure
namespace: default
spec:
entryPoints:
\- websecure
routes:
\- match: Host(\`app.your-domain.com\`)
kind: Rule
middlewares:
\- name: security-headers
\- name: rate-limit
services:
\- name: sample-app-service
port: 80
tls:
certResolver: letsencryptStep 6: Implementing High Availability
For production environments, you need multiple Traefik instances for high availability. Here’s how to configure it:
# ha-traefik-values.yaml
# Extend your existing values file with:
deployment:
replicas: 3
# Pod anti-affinity to spread replicas across nodes
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- weight: 100
podAffinityTerm:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app.kubernetes.io/name
operator: In
values:
- traefik
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
# Horizontal Pod Autoscaler
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 60
- type: Resource
resource:
name: memory
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 70Monitoring and Troubleshooting Your Kubernetes Ingress
Setting up monitoring is crucial for production deployments. Here’s a basic monitoring setup:
# Check Traefik pod status
kubectl get pods -n traefik-system
# View Traefik logs
kubectl logs -n traefik-system deployment/traefik
# Check certificate status
kubectl get certificates -A
# Monitor ingress routes
kubectl get ingressroute -AProblems that happen a lot and how to fix them:
- Provisioning certificates doesn’t work: Make sure that the DNS for your domain is set up correctly and that ports 80 and 443 are open to the internet.
- 503 Service Not Available: Make sure your backend service is operating and that the service selector matches the labels on your pod.
- Can’t get to the dashboard: Check that your DNS is working and that the IngressRoute dashboard is set up.
How to Get Better Performance
To make the most of your Traefik ingress controller:
- Tuning Resources: Check how much CPU and RAM are being used, then alter the limits on those resources if you need to.
- Connection Pooling: Set the correct timeouts and limits on connections for your app’s needs.
- Load Balancing: Use the correct load balancing strategies, like round-robin or least connections, depending on how your traffic flows.
- Caching: Use Traefik middleware to store responses for static content.
Best Ways to Keep Your Data Safe
When deploying in production, it’s crucial to follow security best practices:
- Rules for the Network: Kubernetes Network Policies can help you control how much traffic goes between namespaces.
- RBAC Configuration: Use role-based access control to only provide Traefik the permissions it needs.
- Updates: Always ensure Traefik is running the most recent stable version for security fixes.
- Certificate Monitoring: Set up alerts to let you know when a certificate is about to expire (although Let’s Encrypt should do this for you).
Conclusion
You have successfully built up a Kubernetes ingress controller with Traefik that is ready for production and takes care of TLS certificates on its own. This setup gives you:
- Automatic setting up and renewing of SSL certificates
- Dynamic service discovery and routing
- Advanced middleware features for safety and speed
- Making sure that production workloads are always available
The best thing about this setup is that it can grow with your apps. When you add new services, Traefik will automatically discover and set up routing rules for them based on your IngressRoute configurations.
You should keep an eye on things, create provisions for backing up your certificate storage, and change performance based on what your organization needs.
Taking Your Kubernetes Infrastructure Further
While this guide gets you started with Traefik ingress management, building and maintaining a robust Kubernetes infrastructure involves many moving pieces. From cluster architecture and security hardening to monitoring, observability, and cost optimization, the complexity can quickly become overwhelming for development teams focused on building applications.
At Improwised Tech, we specialize in cloud-native platform engineering solutions that help organizations streamline their Kubernetes operations. Our expertise includes:
DevOps & Platform Engineering: Complete Kubernetes cluster management, CI/CD pipeline optimization, and infrastructure automation that reduces deployment time and operational overhead.
Cloud Infrastructure Management: Multi-cloud strategies, cost optimization, and performance tuning that can reduce your cloud spend by 30-50% while improving application performance.
Security & Compliance: Implementing security-by-design principles, automated compliance monitoring, and vulnerability management across your entire container ecosystem.
Observability & Monitoring: Setting up comprehensive monitoring, logging, and alerting systems that give you complete visibility into your applications and infrastructure health.
Whether you’re struggling with slow deployments, rising cloud costs, or need help scaling your Kubernetes operations, our team of platform engineering experts can help you build a more efficient, secure, and cost-effective infrastructure.
Your next steps should include setting up comprehensive monitoring, implementing backup strategies for your certificate storage, and fine-tuning performance based on your specific workload requirements. If you need guidance on any of these areas or want to discuss how to optimize your entire Kubernetes platform, contact our platform engineering experts for a consultation.
Frequently Asked Question
Get quick answers to common queries. Explore our FAQs for helpful insights and solutions.

November 19, 2025
Unlocking Developer Potential: How Platform Engineering Transforms Developer Experience

By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.


By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.

November 14, 2025
How to Build a High-Impact Internal Developer Platform: Step-by-Step Blueprint, Tools, and Best Practices

By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.
Optimize Your Cloud. Cut Costs. Accelerate Performance.
Struggling with slow deployments and rising cloud costs?
Our tailored platform engineering solutions enhance efficiency, boost speed, and reduce expenses.
