Kubernetes and Platform Engineering: A Match Made in Cloud Heaven

By Angita
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Kubernetes and Platform Engineering: A Match Made in Cloud Heaven
Think of Kubernetes as a powerful engine for running and managing applications packaged in containers – it provides the scalable and dependable foundation that platform engineering needs. This article will explore the technical details of how Kubernetes powers platform engineering, looking at the architecture and the tools that make it all work.
Kubernetes Ecosystem for Platform Engineering
Kubernetes is often referred to as the “platform for building platforms” due to its extensive ecosystem of tools and technologies. The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) provides a suite of vendor-agnostic tools that integrate with Kubernetes, enabling the creation of scalable applications across various cloud environments. This ecosystem includes tools for Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD), observability, operations, AI/ML, security, and storage, all of which work in harmony with Kubernetes to support platform engineering efforts.
Key Components of Kubernetes Ecosystem
CI/CD Tools: Tools like Argo CD and Flux are used for automating the deployment and management of applications on Kubernetes clusters.
Observability Tools: These tools provide insights into application performance and resource utilization, helping platform engineers optimize their platforms.
Operations Tools: Tools such as KubeCost help manage resource costs and utilization within Kubernetes environments.
AI/ML Tools: These tools enable the integration of AI and ML models into applications running on Kubernetes.
Role of Kubernetes in Cloud-Native Platform Development
Kubernetes is pivotal in cloud-native platform development due to its declarative configuration model. This model allows platform engineers to define infrastructure configurations using YAML files, which can be easily updated and deployed. Kubernetes also supports autoscaling and replication, ensuring that platforms can scale according to demand and maintain high availability.
Scalability and Reliability
Scalability: Kubernetes deployments are declarative, making it easy to update configurations and scale resources as needed. Autoscaling and replication capabilities ensure that platforms can handle increased loads without manual intervention.
Reliability: Kubernetes provides replication controllers, schedulers, and load-balancing techniques to ensure that applications remain available even during spikes in demand. Health probes and startup probes enable regular health checks, creating a self-healing system that quickly addresses downtimes.
Platform Engineering Principles with Kubernetes
To maximize the benefits of Kubernetes in platform engineering, several principles should be followed:
Simplify Architecture: Focus on simplifying infrastructure setups. Avoid complex configurations unless necessary, as they can be difficult to manage and troubleshoot.
Leverage Established Cloud Services: Utilize battle-tested cloud Kubernetes services like Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) for easier deployment and troubleshooting.
Standardization: Emphasize standardization across developer teams to ensure a common ground for platform development. This includes using cloud-agnostic Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) and standardized deployments.
DevSecOps and Platform Engineering
Platform engineering is closely tied to DevSecOps practices, as it provides developers with a standardized set of tools and a secure environment for application development. Kubernetes plays a crucial role in this integration by enabling self-service capabilities and automating security practices. Tools like Dynatrace offer automated workflows for deployment validation and anomaly remediation, further improving DevSecOps practices within platform engineering.
Challenges in Implementing Platform Engineering
Despite the advantages of combining Kubernetes with platform engineering, several challenges exist:
Complexity: The integration of multiple tools and technologies within the Kubernetes ecosystem can introduce complexity, requiring careful management and monitoring.
Resource Utilization: Ensuring efficient resource utilization across diverse environments can be challenging without proper visibility and management tools.
Security: Maintaining security across a containerized environment involves managing various security components and ensuring compliance with organizational policies.
Conclusion
The combination of Kubernetes and platform engineering offers a robust foundation for building scalable and reliable infrastructure platforms. By understanding the technical aspects of this integration, organizations can better navigate the challenges involved. However, the consequences of not adopting these practices can be significant:
The absence of standardized platforms can lead to a number of challenges. Firstly, resource use may be inefficient, with resources being underutilized or wasted, driving up operational costs. Secondly, inadequate security measures can expose applications to vulnerabilities, potentially resulting in data breaches or service disruptions. Finally, without self-service platforms, developers may spend more time on infrastructure management tasks, hindering their ability to focus on application development and innovation


By Angita
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.
Wed Mar 12 2025
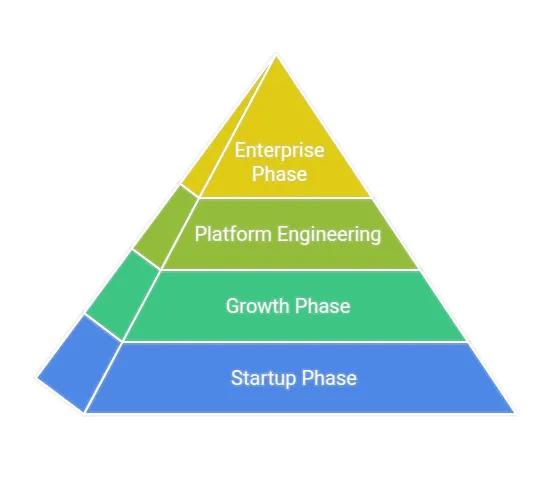
From Startup to Enterprise: Scaling Your Tech Infrastructure with Platform Engineering

By Angita
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.


By Angita
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.
Optimize Your Cloud. Cut Costs. Accelerate Performance.
Struggling with slow deployments and rising cloud costs?
Our tailored platform engineering solutions enhance efficiency, boost speed, and reduce expenses.