April 3, 2025
CI/CD in Air-Gapped Environments: Running Pipelines Without Internet Access

By Rakshit Menpara
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
CI/CD in Air-Gapped Environments: Running Pipelines Without Internet Access
Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate the software development lifecycle by integrating code changes, running tests, and deploying updates. These pipelines are typically designed for environments with internet access, but some industries operate within air-gapped networks—isolated environments with no direct internet connection. This article explores the technical complexities of implementing CI/CD in these secure environments.
Challenges in Implementing CI/CD in Air-Gapped Environments
1. Managing Source Code and Version Control
Traditional development teams rely on cloud-based Git repositories such as GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket. In an air-gapped setup:
A self-hosted version control system (such as GitLab CE or Gitea) must be deployed within the isolated environment. Developers must manually synchronize code changes between external and internal networks using offline media (USB drives, DVDs, or controlled file transfers).
Automated webhooks and CI triggers commonly used in cloud-based systems must be replaced with internal job schedulers or event-driven mechanisms.Without an efficient source control strategy, teams may face delayed collaboration, lack of version tracking, and increased risk of code conflicts.
2. Handling Dependencies Without Internet Access
Modern software development depends on external libraries and frameworks managed via package managers like npm, pip, Maven, NuGet, and others. In an air-gapped CI/CD pipeline:
-
A local mirror of required dependencies must be maintained using tools like Nexus Repository, Artifactory, or an internal package registry.
-
Regular updates to dependencies must be carefully planned, requiring a manual import process to bring in security patches and performance improvements.
-
Development teams must proactively manage dependency resolution to prevent build failures caused by missing or outdated libraries.
Without a structured approach to dependency management, teams risk using outdated software components that could lead to security vulnerabilities or incompatibility issues.
3. Artifact Storage and Build Management
CI/CD pipelines typically fetch dependencies, compile source code, and generate build artifacts, which are then stored in external artifact repositories. In an air-gapped system:
All builds must be performed on self-hosted CI servers, such as Jenkins, GitLab Runner, or TeamCity, without external dependencies. A local artifact repository must be established to store compiled binaries, libraries, and other deliverables.
Secure validation mechanisms must be implemented to prevent unauthorized or tampered artifacts from entering production environments. Lack of a robust artifact management process can lead to inefficiencies in deployment and increase security risks from unverified builds.
4. Containerization and Image Management
Many modern applications are deployed as containers using Docker or Kubernetes. In an air-gapped environment:
A self-hosted container registry (such as Harbor, Nexus, or a private Docker registry) is required. Approved container images must be manually imported and periodically updated from external sources.Image signing and verification must be enforced to prevent the introduction of compromised software.
Failing to maintain an up-to-date internal container registry can lead to outdated, vulnerable, or incompatible application environments.
5. Automated Testing and Security Validation
Continuous testing is a critical component of CI/CD, ensuring that changes do not introduce defects or security vulnerabilities. In air-gapped environments:
-
Static code analysis, dynamic analysis, and unit tests must be conducted using locally hosted tools.
-
Security scanning engines (such as SonarQube, OWASP Dependency-Check, and SAST tools) must have offline rule sets and scanning capabilities.
-
Logging and monitoring systems must be configured to provide real-time insights without relying on external cloud-based logging services.
A lack of automated testing and security validation can result in undetected vulnerabilities and lower software quality.
6. Deployment and Configuration Management
Deploying applications without internet access requires significant adjustments to traditional workflows:
Configuration management tools (such as Ansible, Puppet, or Chef) must operate solely within the air-gapped network. Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) must be managed using internal repositories, with Terraform and other tools pointing to pre-approved local module libraries. Deployment rollback strategies must be carefully implemented, as cloud-based rollback services are unavailable.
Failure to manage configurations properly can result in misconfigured environments, increased deployment failures, and difficulty in rolling back changes.
Strategies for Implementing CI/CD in Air-Gapped Environments
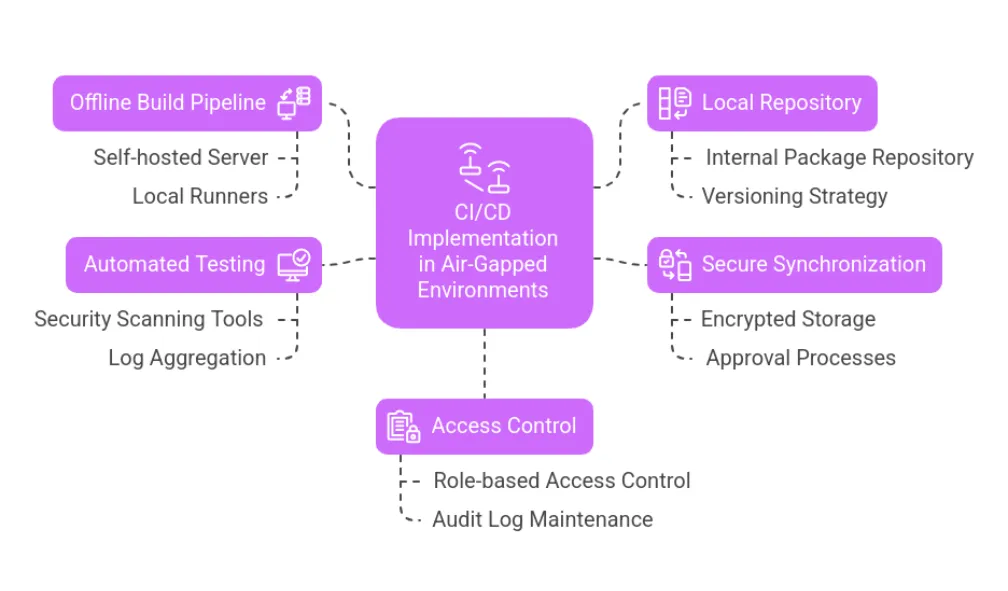
1. Establishing an Offline Build Pipeline
-
Deploy a self-hosted CI/CD server
-
Configure local runners without external dependencies
-
Implement internal automation for build triggers
2. Maintaining a Local Package and Artifact Repository
-
Host an internal package repository
-
Automate the import process for security patches
-
Establish version tracking for components
3. Secure Offline Synchronization of Updates
-
Use encrypted storage devices for transfers
-
Define strict approval processes for imports
-
Regularly audit imported packages
4. Implementing Automated Testing and Security Verification
-
Maintain offline security scanning tools
-
Configure quality gates in CI pipelines
-
Establish internal log aggregation
5. Enforcing Access Control and Compliance
-
Implement strict role-based access control
-
Maintain audit logs of CI/CD actions
-
Conduct regular compliance assessments
Consequences of Poor Implementation
Security Risks
Improper dependency management can lead to vulnerable or outdated software.
Operational Overhead
Manual synchronization introduces inefficiencies and human error potential.
Delayed Releases
Lack of automation slows down the development lifecycle.
Higher Maintenance Costs
Air-gapped pipelines require dedicated resources for upkeep.
Limited Scalability
Additional hardware demands constrain growth compared to cloud solutions.
Conclusion
Organizations that fail to properly design and implement CI/CD pipelines in air-gapped environments face multiple consequences. Security risks arise when dependencies and artifacts are not managed properly, leading to the deployment of vulnerable or outdated software. Increased operational overhead results from the need for manual synchronization of updates and packages, introducing inefficiencies and the potential for human error.
Delayed software releases occur due to the absence of automated build and test capabilities, slowing down the overall development lifecycle. Higher maintenance costs are another issue, as maintaining an air-gapped CI/CD pipeline requires dedicated resources for dependency management, infrastructure upkeep, and compliance enforcement. Additionally, limited scalability becomes a challenge since traditional cloud-based CI/CD pipelines scale effortlessly, whereas air-gapped environments demand additional hardware and maintenance, constraining growth.
To mitigate these challenges, organizations must invest in a robust strategy for self-hosted infrastructure, controlled update mechanisms, and comprehensive security validation. Properly designed CI/CD pipelines in air-gapped environments can ensure reliable software delivery while maintaining compliance and security requirements.

November 19, 2025
Unlocking Developer Potential: How Platform Engineering Transforms Developer Experience

By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.


By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.

November 14, 2025
How to Build a High-Impact Internal Developer Platform: Step-by-Step Blueprint, Tools, and Best Practices

By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.
Optimize Your Cloud. Cut Costs. Accelerate Performance.
Struggling with slow deployments and rising cloud costs?
Our tailored platform engineering solutions enhance efficiency, boost speed, and reduce expenses.
