April 7, 2025
Self-Healing CI Pipelines: How to Auto-Diagnose & Fix Build Failures Without Human Intervention

By Rakshit Menpara
Improwised Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines automate software build and test processes, ensuring that code changes are validated before deployment. However, build failures can disrupt development workflows, increasing delays and requiring manual intervention. Self-healing CI pipelines detect, diagnose, and remediate failures without human oversight, maintaining efficiency and reducing downtime.
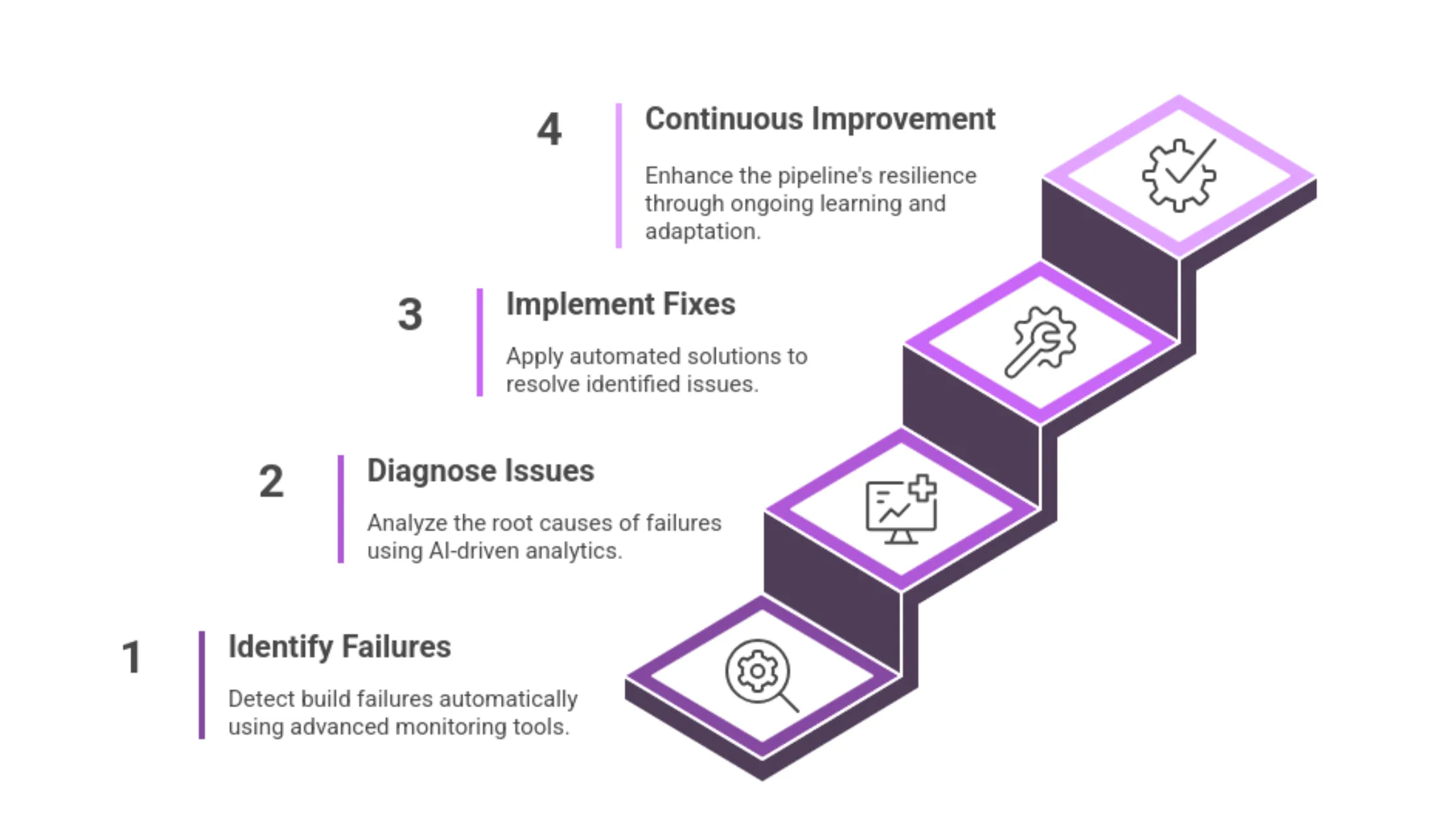
Automated Failure Diagnosis
Self-healing CI pipelines use automated failure diagnosis to identify issues. This process involves log analysis, anomaly detection, and root cause analysis (RCA).
Log Analysis
Logs generated during builds contain valuable data for identifying failures. Automated parsers extract relevant information by detecting error patterns and failure signatures. Tools like ELK Stack and Fluentd aggregate logs for real-time inspection.
Anomaly Detection
Machine learning models trained on historical build data identify deviations from normal build patterns. Techniques such as unsupervised learning, isolation forests, and autoencoders detect anomalies in build times, test durations, and dependency resolution.
Root Cause Analysis
-
Static and dynamic analysis: Tools like SonarQube and runtime profilers help detect issues before and during execution.
-
Heuristic-based troubleshooting: Rule engines match known error patterns to suggest likely causes.
-
Dependency impact analysis: Identifies breakages caused by third-party libraries or version conflicts.
Automated Remediation Strategies
Once an issue is diagnosed, remediation strategies are applied automatically based on predefined recovery actions.
Retry Mechanisms
Transient failures—such as network instability, flaky tests, or temporary infrastructure outages—can be resolved with automated retry mechanisms. Retry policies define backoff strategies, including exponential backoff and jitter to prevent cascading failures.
Code Reversion
When a newly introduced change breaks the build, automated rollback mechanisms revert the commit. Git-based workflows use git bisect to isolate problematic commits, and CI tools like Jenkins and GitHub Actions trigger automated rollbacks.
Container and Environment Recovery
For infrastructure-related failures, automated remediation may include:
-
Container restarts: Restarting misconfigured or failed containers.
-
Reprovisioning ephemeral environments: Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC) tools like Terraform and Kubernetes Operators redeploy failing environments.
Dependency Conflict Resolution
Dependency mismatches can break builds. Self-healing pipelines resolve dependency conflicts by:
-
Version pinning: Enforcing known stable versions.
-
Automated dependency updates: Bots like Dependabot and Renovate identify and apply fixes.
Flaky Test Detection and Management
Flaky tests cause intermittent failures. Techniques to handle them include:
-
Quarantine and re-execution: Flaky tests are identified, marked, and re-executed under controlled conditions.
-
Historical analysis: CI systems track past failures to determine if a test consistently exhibits instability.
Implementation of Self-Healing in CI Pipelines
Machine Learning-Driven Failure Classification
Supervised learning models classify build failures based on historical labeled datasets. Models trained with techniques such as decision trees, random forests, and neural networks predict failure types.
Predictive Analysis for Proactive Recovery
Predictive models analyze CI pipeline trends to anticipate failures before they occur. Anomalous patterns in build duration, resource consumption, or test execution are flagged.
Auto-Scaling Infrastructure
Dynamic resource allocation ensures that CI/CD environments scale in response to workload demands. Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) adjusts pod replicas based on CPU or memory usage, preventing build failures due to resource exhaustion.
Integrating Observability
Monitoring tools provide real-time insights into pipeline health:
-
Prometheus and Grafana: Collect and visualize CI pipeline metrics.
-
Jaeger and OpenTelemetry: Trace execution flows to identify bottlenecks.
-
Alerting systems: Automated notifications with PagerDuty or Slack inform developers when remediation attempts fail.
Conclusion
Self-healing CI pipelines minimize downtime by diagnosing and resolving failures without manual intervention. However, implementing automated remediation requires robust logging, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics. Over-reliance on automation without sufficient validation can lead to unintended consequences, such as unnecessary rollbacks or masking underlying code defects. Additionally, improper failure classification may trigger incorrect remediation strategies, causing further disruptions. Balancing automation with controlled oversight ensures that self-healing mechanisms improve reliability while maintaining software quality.

November 19, 2025
Unlocking Developer Potential: How Platform Engineering Transforms Developer Experience

By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.


By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.

November 14, 2025
How to Build a High-Impact Internal Developer Platform: Step-by-Step Blueprint, Tools, and Best Practices

By Shyam Kapdi
Improwised Technologies
Pvt. Ltd.
Optimize Your Cloud. Cut Costs. Accelerate Performance.
Struggling with slow deployments and rising cloud costs?
Our tailored platform engineering solutions enhance efficiency, boost speed, and reduce expenses.
